Practical structure prediction with AlphaFold 3, Boltz 2 and ChimeraX
Tom Goddard
September 4, 2025
Pacific Northwest Cryo-EM Center workshop. Video of talk.
Topics
- Structure prediction and cryoEM
- How to run predictions with limited computer resources
- Many machine learning structure prediction programs. Why Boltz?
- Demonstrate Boltz run from ChimeraX on Mac
- Demonstrate Boltz on Mac advanced features
- Limitations of Boltz on Mac, Windows and Linux
- AlphaFold 3 for predicting large complexes
- Questions and answers
Structure prediction and cryoEM
How is structure prediction useful for cryoEM?
- Make starting models for refinement in cryoEM maps.
- Identify probable disordered regions of proteins.
- Test binding of accessory proteins.
- Structure prediction increases the need for cryoEM
by hinting at mechanisms for many more complexes that
lead to experimental investigation. "A rising tide lifts all boats."
How to run predictions with limited computer resources
Structure predictions can be run in many ways.
- Web services (e.g. Google's AlphaFold 3 server)
- Cloud virtual machines (e.g. Colabfold on Google Colab)
- Academic computing clusters (e.g. UC San Francisco Wynton high performance cluster)
- Desktop computers running Linux with expensive AI GPUs (e.g. Nvidia H100 GPU $30,000).
- On typical Mac, Windows or Linux personal computers (e.g. laptops).
I want to talk about practical ways for academic basic science researchers
to run predictions with commonly available personal computers.
- Efficient - taking minutes, rather than an hour on a shared computer system.
- Flexible - full access to all features, not a blackbox, permissive license terms.
Many machine learning structure prediction programs. Why Boltz?
Here are some of the most commonly mentioned machine learning structure prediction efforts.
Most are projects are commercial by developers with AI expertise and not known for biology.
- AlphaFold - developed by Google DeepMind.
- Chai - developed by ChaiDiscovery, venture capital funded startup ($70 million funding in Aug 2025).
- HelixFold - developed by Baidu, the equivalent of Google in China.
- Protenix - developed by ByteDance, developer of TikTok.
- OpenFold - developed by a consortium of academics and 30 pharmaceutical companies.
- Boltz - developed by an MIT lab and Recursion Pharmaceuticals drug discovery company.
- RosettaFold All-Atom - University of Washington lab.
I've been working mostly with Boltz the past 6 months guessing it will be the most actively developed
by academic researchers (20 developers contributing code June-Aug 2025).
Demonstrate Boltz run from ChimeraX on Mac
I'll demonstrate how to run Boltz predictions on a Mac computer from ChimeraX.
Details.
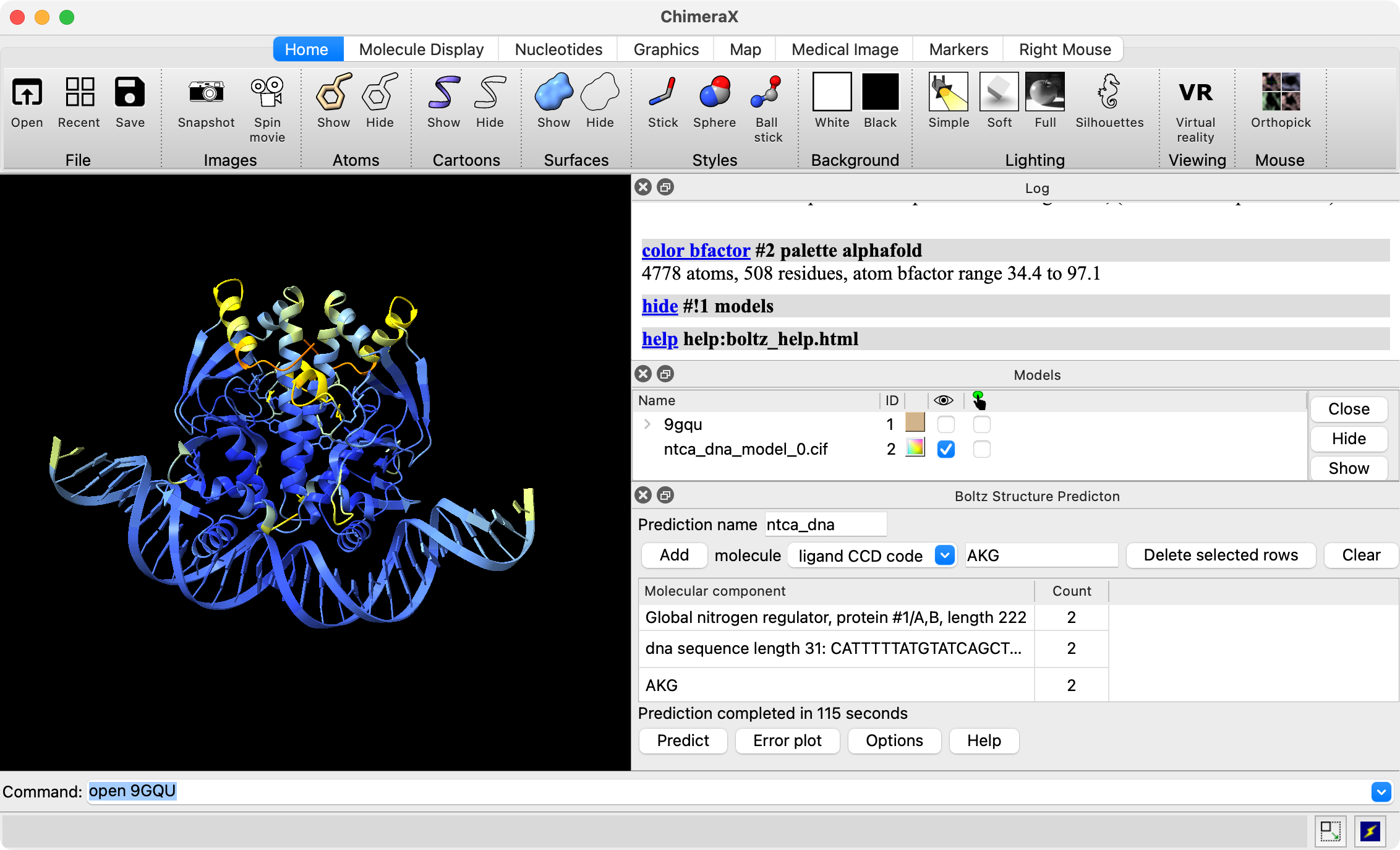
- First time using Boltz in ChimeraX (daily build) will show Install button to install Boltz 2.2.
- Run prediction of a transcription factor protein dimer (sequence), DNA (sequence) and small-molecule activator (3-letter code AKG).
Video.
- Takes about 2 minutes for structure, 1 minute for affinity.
- Examine confidence scores pLDDT, PAE, ipTM, binding affinity and probability.
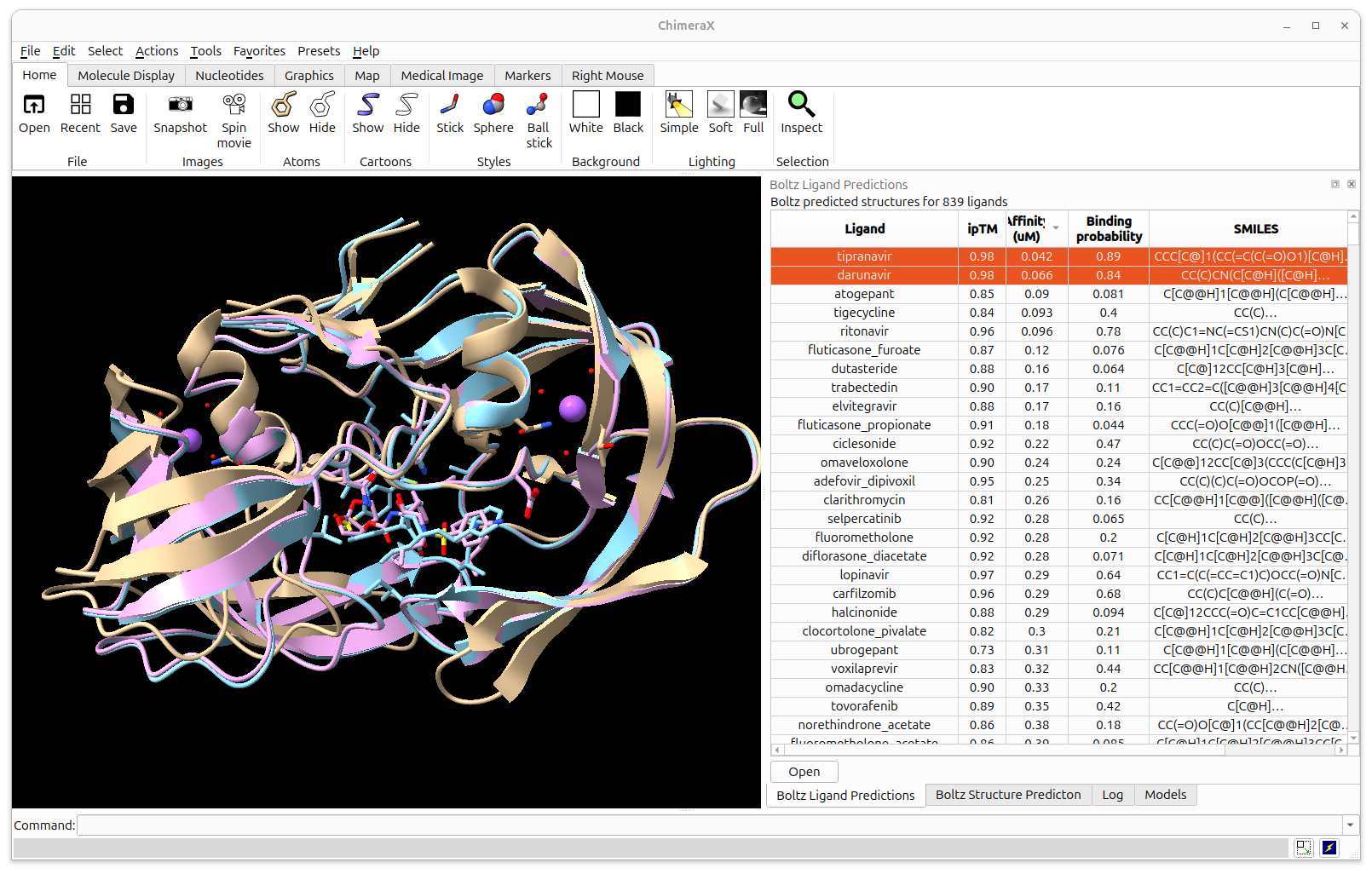
ChimeraX can predict a series of small molecules bound to a molecular assembly, estimating binding affinity.
Video.
|
Boltz advanced features

Boltz has many interesting prediction capabilities.
Documentation.
Some allow using additional experimental information to steer the prediction.
- Pocket specification.
- Distance restraints between atoms (e.g. known from mass spectroscopy cross-links).
- Template structures with distance tolerance.
Some allow modifications to proteins and nucleic acids.
- Post-translational modifications, e.g. phosphorylation.
- Covalently bound ligands.
Some effect conformational sampling.
- Dynamic prediction mode based on NMR and MD trajectory training.
- Custom multiple sequence alignment input.
ChimeraX does not currently have user interfaces to use these capabilities
but it is relatively easy to modify Boltz input created by ChimeraX and run Boltz outside of ChimeraX.
Examples on Boltz Github.
I'll show an example of how to methylate a DNA residue (cytosine 14 in NTCA example).
Limitations of Boltz on Mac, Windows and Linux
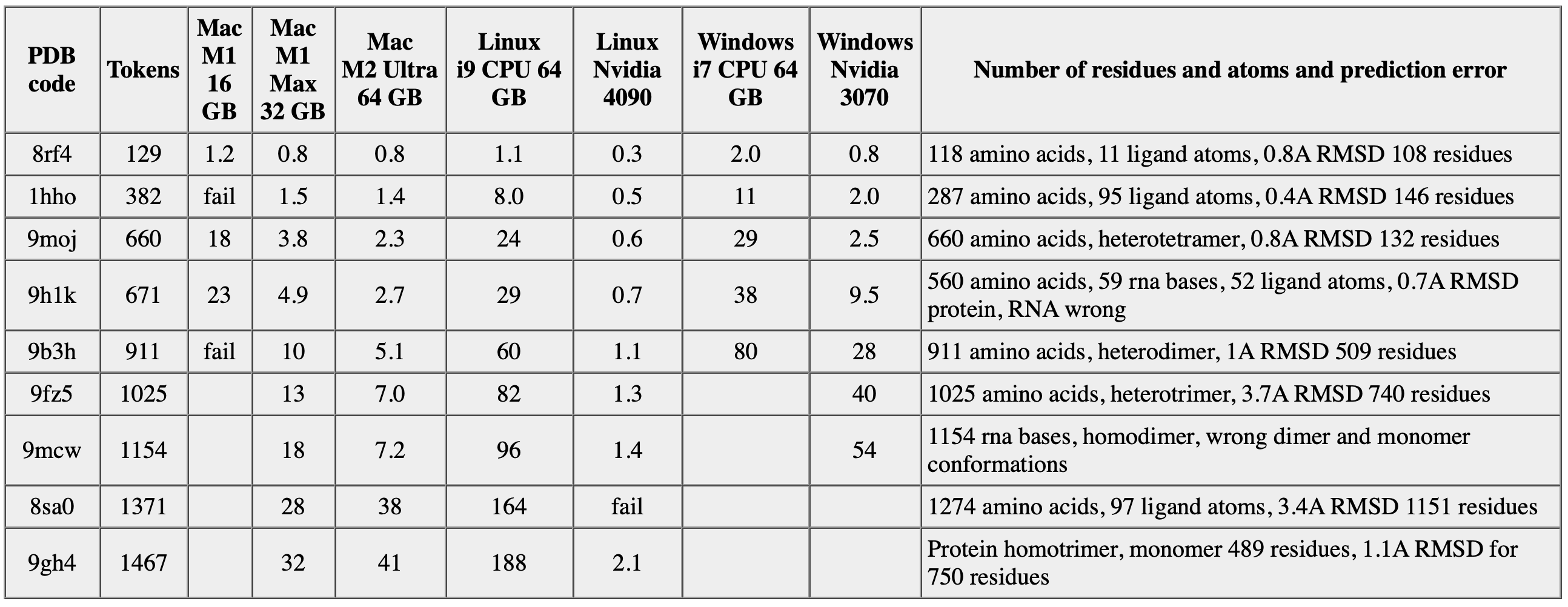
Boltz prediction times in minutes.
Tokens is number of standard polymer residues plus ligand atoms.
|
It is only be possible to predict modest size molecular complexes on low-power computers.
Boltz predictions use a lot of memory and rely heavily on GPU or CPU compute speed.
- Typical sizes and run times.
- Mac laptop with 16 GB of memory, 600 residues, few small ligands, taking up to 20 minutes.
With 32 GB up to 1300 residues.
- Windows, 400 residues 10 minutes with only CPU or 2 minutes with Nvidia 3070 GPU, 700 residues 30 minutes with only CPU, 10 minutes with Nvidia 3070 GPU
- Linux with Nvidia 4090 GPU, up to 1300 residues in 2 minutes, with only CPU similar to Windows.
Runtimes for demonstration NTCA + DNA + 2-oxoglutarate structure and affinity prediction:
- 1 minutes, Linux Nvidia 4090
- 3.5 minutes, Mac Studio M2 Ultra
- 4 minutes, Windows Nvidia 3070
- 6 minutes, MacBook Pro M1 Max
- 21 minutes, Linux Intel i9-13900K CPU
- 25 minutes, Mac Mini M1 16GB
- 28 minutes, Windows Intel i7-12700K CPU
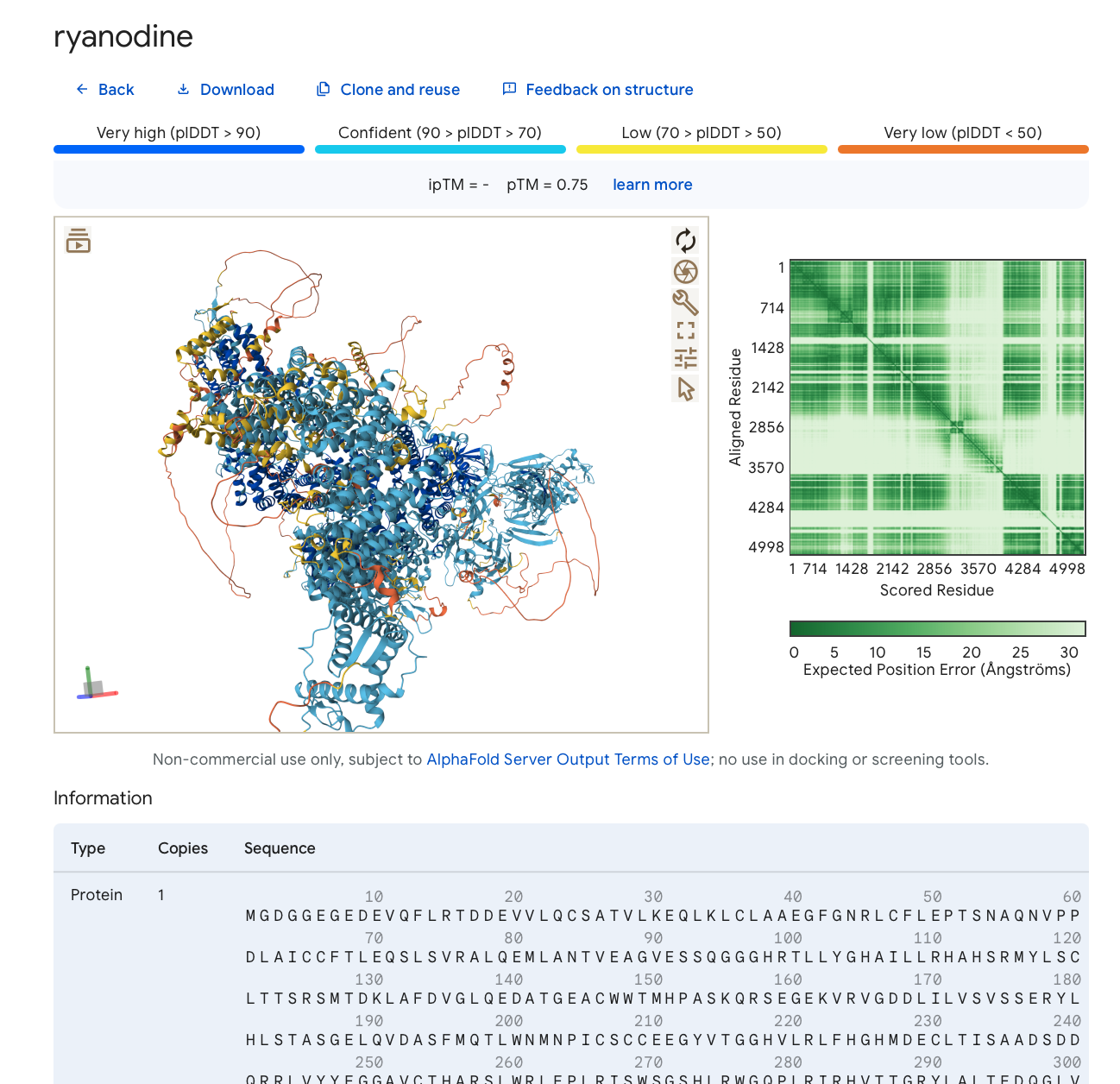
Ryanodine receptor monomer 5000 residue prediction shown by AlphaFold 3 server.
|
AlphaFold 3 for predicting large complexes
AlphaFold 3 is much better optimized than Boltz for predicting large molecular assemblies.
- Can predict up to 5000 residues using Google AlphaFold 3 server in about 30 minutes to 4 hours (depending on server load) using a free Google account.
- Server does not allow arbitrary ligands, only few dozen most common ligands.
- No commercial use allowed.
Questions and answers
Take questions from audience.
Some interesting topics.
n





